In the realm of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, the terms “alternator” and “generator” often emerge as focal points of discussion.
At first glance, they may seem interchangeable due to their fundamental purpose. However, a closer inspection reveals distinct differences that set them apart.
This alternator vs generator article aims to demystify these two components, shedding light on their functionalities, applications, and how to choose between them based on specific requirements.
Understanding Alternators
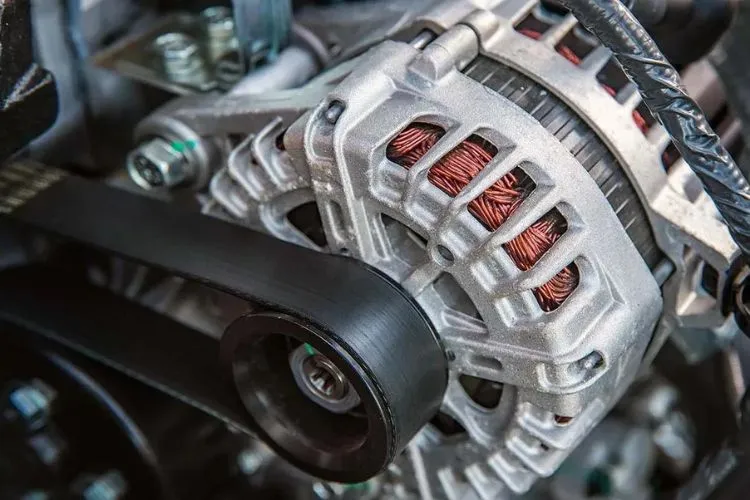
An alternator is a type of electrical generator designed to convert mechanical energy into alternating current (AC).
The core principle of operation lies in electromagnetic induction, where a rotating magnetic field interacts with a stationary armature or vice versa. This process generates AC voltage consistently.
Alternators are prevalent, especially in automotive applications, where they play a crucial role in charging the vehicle’s battery and powering the electrical system when the engine runs.
They come in various forms, tailored to different applications, including those in diesel-electric locomotives and marine engines.
One of the key features of alternators is their efficiency and the ability to generate power at both low and high speeds.
This efficiency stems from their capacity to produce AC power, which can easily be transformed into the desired voltage levels, thereby minimizing energy loss during conversion.
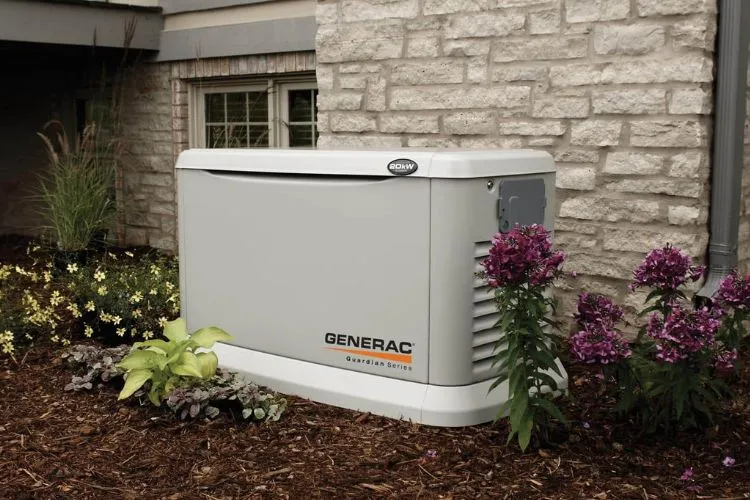
Understanding Generators
Generators, in their broadest sense, convert mechanical energy into electrical energy but do so in the form of direct current (DC).
The mechanism involves electromagnetic induction, where movement within a magnetic field induces an electric current in a wire loop.
The types of generators are diverse, each suited to specific scenarios. Standby generators provide emergency power during power outages, while portable generators offer electricity for camping or job sites.
The defining characteristic of generators is their ability to produce a steady power output. This makes them ideal for applications that require uninterrupted power supply.
However, they generally weigh more and have lower efficiency compared to alternators.

Alternator vs Generator: Comparing The Two
Similarities
The foundational similarity between alternators and generators is their role in energy conversion. Both devices harness mechanical energy to produce electrical energy, pivotal in countless applications.
Differences
Construction and Design:
Alternators and generators differ markedly in design. Alternators typically have a more complex construction, optimized to generate AC power efficiently. In contrast, generators have a simpler design suited to DC power production.
Energy Output:
The most striking difference lies in their output; alternators produce AC, while generators yield DC. This distinction deeply influences their applications and performance characteristics.
Efficiency and Durability:
Alternators generally offer higher efficiency and durability. Their ability to produce power at various engine speeds without significant loss extends their lifespan and reduces maintenance needs.
Applications:
Alternators fill the engine bays of most modern vehicles due to their efficient power generation at variable speeds. Generators, however, find their niche in providing emergency backup and portable power, where steady DC output is paramount.
Maintenance and Cost:
Generators typically require more frequent maintenance and are costlier to run. Conversely, alternators, with their higher upfront cost, often prove more economical over their lifespan due to lower maintenance and operational expenses.
Pros and Cons of Alternators
Pros
✅ Alternators excel in efficiency and adaptability, capable of meeting the power demands of various applications while minimizing energy loss.
Cons
❌ The complexity of alternators can be a double-edged sword, potentially complicating repairs and requiring more sophisticated control systems.
Pros and Cons of Generators
Pros
✅ Generators stand out for their simplicity and reliability, capable of providing a steady DC output crucial for many critical applications.
Cons
❌ The trade-off comes in the form of weight, efficiency, and often a higher operational cost, making them less suited for applications that benefit from the efficiency and variable output of alternators.
Making the Right Choice
Deciding between an alternator and a generator hinges on the specific needs of the application.
Consider the type of electrical energy required (AC or DC), the operational efficiency, durability, maintenance, and cost implications.
For automotive applications or scenarios requiring high efficiency and variable power output, an alternator is the way to go.
In contrast, for emergency backup power or portable solutions where DC power is essential, a generator might be the better option.
Maintenance Schedules
Regular Maintenance
To ensure longevity and optimal performance, alternators should be inspected annually for wear and secure connections, while generators require checks every 50 hours of use, including oil changes and filter replacements.
Regular cleaning to avoid dirt buildup is imperative for both.
Professional Services
Engage professional services for a comprehensive inspection of alternators and generators every two years or after any sign of malfunction, such as power fluctuations or unusual noises. Experts can handle complex issues and ensure that all components function efficiently and safely.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the key difference between an alternator and a generator?
The core difference lies in their output; alternators produce alternating current (AC), while generators produce direct current (DC).
Can an alternator be used in place of a generator?
This depends on the application’s specific requirements regarding the type of electrical output needed.
What are the signs of a failing alternator or generator?
Common signs include dimming lights, battery discharge, and unusual noises, indicating the need for inspection or maintenance.
How do I maintain an alternator or generator?
Regular checks for wear and tear, ensuring clean connections, and in the case of generators, routine oil and filter changes are essential.
Which is more cost-effective in the long run, an alternator or a generator?
Although alternators may have a higher upfront cost, their efficiency and lower maintenance needs can make them more economical over time.
Conclusion:
While alternators and generators play similar roles in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, their differences in output, efficiency, application, and cost make them suited to distinct scenarios.
Understanding these nuances is crucial in selecting the right component for your needs, ensuring reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
