Generators are indispensable tools that provide electricity during power outages, ensuring that our lives, businesses, and critical infrastructure remain operational.
There’s a variety of generators available, with diesel and gasoline models being among the most common for personal, commercial, and small-scale industrial use.
This comprehensive guide dives deeper into the nuances of the debate of diesel vs gasoline generators, comparing them across various parameters to help users make well-informed decisions tailored to their specific power generation needs.

Diesel Generators: A Closer Look
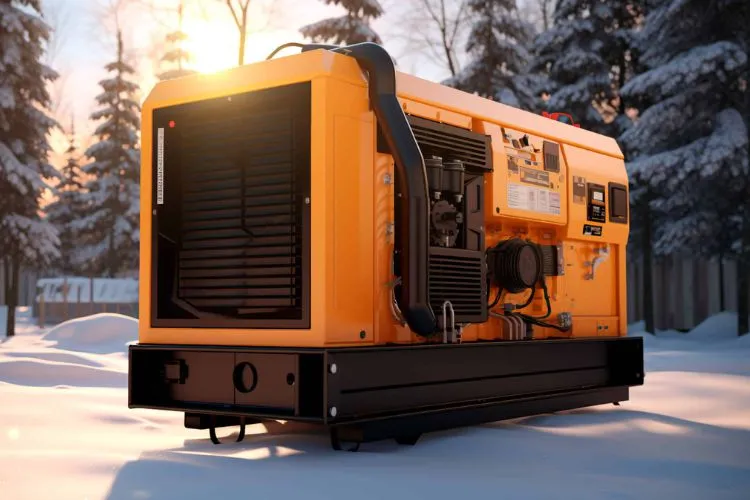

What are Diesel Generators?
Diesel generators use diesel fuel to generate electrical power. They are revered for their efficiency and durability, thanks to the rugged build of diesel engines, which can withstand prolonged usage and harsh operational conditions.
Advantages of Diesel Generators
Durability and Longevity
Diesel generators boast superior build quality that translates to longer operational life. They are designed to withstand rigorous usage, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent, long-term power supply.
Fuel Efficiency
One of the hallmark benefits of diesel generators is their fuel efficiency. They have a higher power output per liter of fuel compared to gasoline generators, which results in longer operation times on the same amount of fuel.
Low Maintenance Requirements
Without the need for spark plugs or carburetors, diesel engines are comparatively simpler and require less frequent maintenance. This reduces the overall cost of keeping the generator in prime working condition.
Disadvantages of Diesel Generators
Higher Initial Cost
The robustness and efficiency of diesel generators come at a higher upfront cost, making them a significant initial investment.
Noise and Emissions
Traditionally, diesel generators are louder and produce more emissions than their gasoline counterparts, posing considerations for residential use and environmental impact.
Fuel Accessibility and Storage
While diesel is less volatile than gasoline, it still requires proper storage conditions, and accessibility might be an issue in certain regions.
Gasoline Generators: An Overview
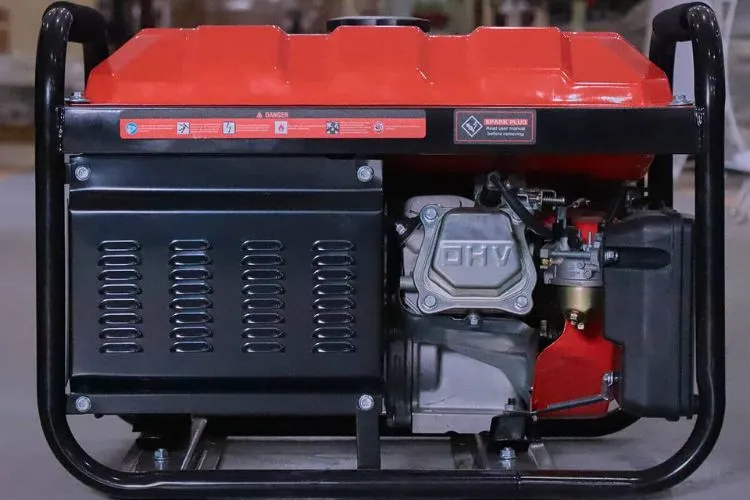
Understanding Gasoline Generators
Gasoline generators are powered by gasoline, a widely available fuel. They are known for their ease of use and have been a popular choice for backup power in homes and small businesses.
Advantages of Gasoline Generators
Lower Initial Investment
Compared to diesel generators, gasoline models are more affordable upfront, making them accessible to a broader audience.
Fuel Availability
Gasoline is readily available in most areas, making it convenient for emergency power needs where fuel accessibility is crucial.
Portability and Versatility
These generators are available in various sizes, including more compact options that are easier to move and store, providing flexibility in usage.
Challenges with Gasoline Generators
Fuel Efficiency and Operating Costs
Gasoline generators are not as fuel-efficient as diesel models, which can lead to increased operational costs over time due to higher fuel consumption.
Durability and Maintenance
They generally have a shorter lifespan and may require more frequent maintenance, impacting long-term reliability and cost.
Safety and Fuel Shelf Life
Gasoline’s high volatility presents more significant risks in storage and handling. It also degrades faster than diesel, affecting long-term storage.
Diesel vs Gasoline Generators: Direct Comparison
When comparing diesel and gasoline generators, it’s crucial to consider several key areas:
- Cost: Gasoline generators may have a lower upfront cost, but diesel generators often offer better long-term value due to their efficiency and durability.
- Fuel Efficiency: Diesel generators excel in power output per unit of fuel, making them more economical in extended use.
- Maintenance: Diesel units come out ahead with less frequent maintenance needs, though routine checks are vital for both types.
- Durability: Diesel generators typically offer a longer lifespan due to their robust construction and operational efficiency.
Choosing the right generator requires a balanced consideration of immediate needs, long-term goals, fuel availability, and operational costs.
Critical Factors for Selection

Assessing Power Requirements
The first step in choosing between a diesel and gasoline generator is evaluating your power needs. For higher demand or continuous operation, diesel generators are better suited due to their efficiency and durability.
Budget Considerations
Though gasoline generators are less expensive initially, the total cost of ownership including fuel, maintenance, and potential replacement needs to be considered. Diesel generators, despite their higher upfront cost, may provide savings over time.
Fuel Availability and Storage
Your local availability of diesel or gasoline can greatly influence your choice. Also, consider the storage requirements and safety considerations for the fuel type you select.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Your ability and willingness to perform regular maintenance can influence your choice. Gasoline generators may require more frequent care, while diesel models generally demand less attention but benefit from professional servicing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which generator is more cost-effective in the long run?
Diesel generators tend to be more cost-effective over time, thanks to their fuel efficiency and longer lifespan, despite the higher initial investment.
Can I use these generators indoors?
No, running generators indoors is unsafe due to carbon monoxide risks. Always operate them in well-ventilated outdoor locations.
How often do I need to perform maintenance on these generators?
Gasoline generators usually require more frequent maintenance than diesel models. However, all generators need regular checks and servicing to ensure safe, efficient operation.
What is the environmental impact of these generators?
Diesel generators have traditionally produced more emissions, but advancements are reducing their environmental footprint. Gasoline also has environmental concerns, particularly with storage safety and fuel volatility.
How should I store fuel safely?
Follow local guidelines and best practices for fuel storage, ensuring gasoline is kept in approved containers and diesel is stored in a cool, well-ventilated place away from direct sunlight.
Conclusion:
Selecting between a diesel and gasoline generator involves a nuanced consideration of your specific needs, the operational environment, fuel availability, and financial factors.
Diesel generators are typically favored for their longevity, fuel efficiency, and lower maintenance, making them suitable for demanding or continuous applications.
Conversely, gasoline generators offer a cost-effective solution for less intensive uses, benefiting from greater fuel accessibility and portability.
This comprehensive comparison aims to equip you with the knowledge to choose the most appropriate backup power solution.
Beyond the initial costs and specifications, consider the long-term implications, regular upkeep, and safety practices associated with the generator type you select.
